The rugby 9 position is a crucial one on the field, demanding a unique blend of skill, agility, and decision-making. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of the number 9 role, exploring its variations across rugby codes, examining the impact of legendary players, and providing insights into training, strategies, and future trends.
Understanding the Role of the Number 9 Position in Rugby
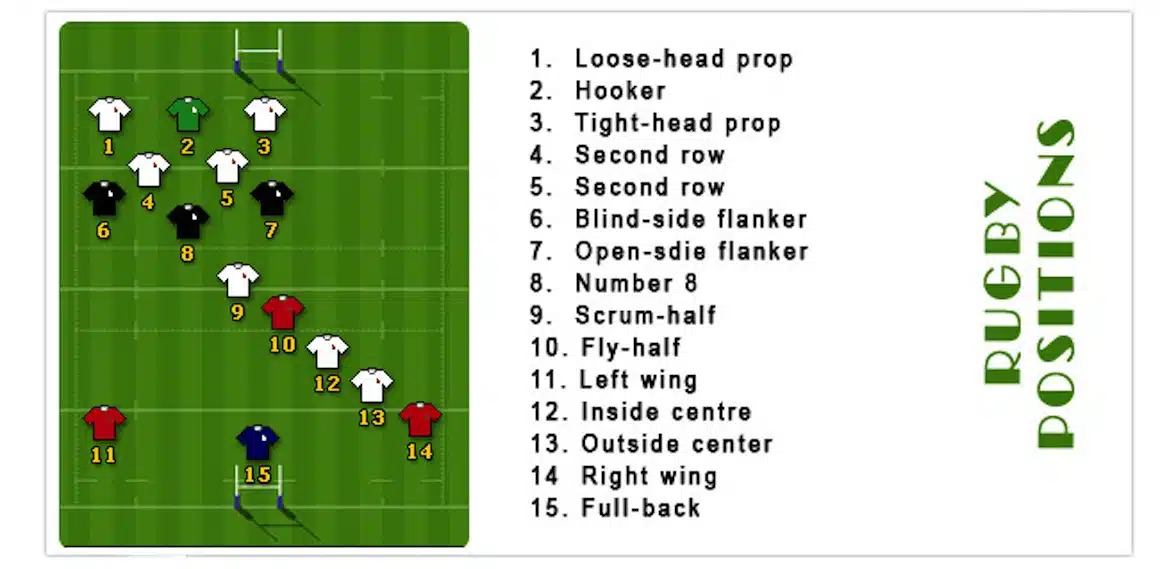
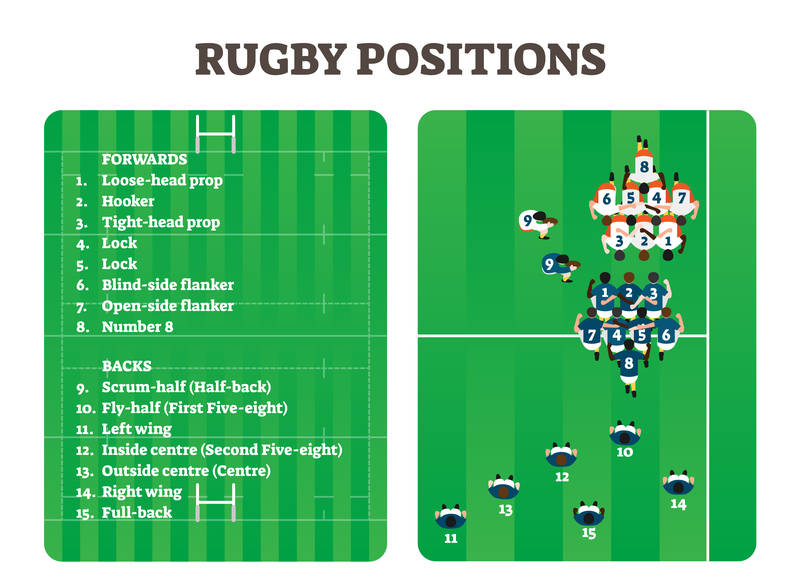
The number 9 position in rugby is a crucial one, with the player holding the primary responsibility for distributing the ball from the scrum and line-out. This position demands a unique blend of technical skills, decision-making abilities, and physical attributes.
Key Responsibilities
The primary responsibilities of a number 9 include:
- Hooking the ball in the scrum and throwing it to the scrum-half.
- Receiving the ball from the line-out and passing it to the fly-half or other players.
- Making quick and accurate decisions on how to distribute the ball.
- Communicating effectively with teammates to ensure a smooth flow of play.
Essential Skills and Attributes
To excel in the number 9 position, players must possess the following skills and attributes:
- Excellent throwing skills, both short and long distances.
- Exceptional handling skills and the ability to make quick decisions.
- Strong leadership and communication skills.
- Good fitness and agility.
- A deep understanding of the game’s tactics and strategies.
Variations in the Number 9 Position Across Different Rugby Codes
The number 9 position in rugby union and rugby league shares some similarities but also exhibits distinct variations in responsibilities and gameplay.
Rugby Union
In rugby union, the number 9 is known as the scrum-half and plays a crucial role in directing the team’s attack from the base of the scrum. They are responsible for feeding the ball into the scrum, distributing it to the backs, and making tactical decisions.
Rugby League
In rugby league, the number 9 is known as the hooker and has a more limited role compared to their rugby union counterpart. They are primarily responsible for hooking the ball out of the scrum and passing it to the halfback.
However, they may also be involved in attacking plays as a dummy-half runner or support player.
Unique Aspects
One of the key differences between the scrum-half and hooker positions is their involvement in the breakdown. In rugby union, the scrum-half is expected to compete for the ball at the breakdown, while in rugby league, the hooker typically remains outside the ruck to support the attacking team.
Another difference lies in their kicking abilities. Scrum-halves in rugby union are often skilled kickers who can use their kicking game to gain territory or create attacking opportunities. In contrast, hookers in rugby league are rarely involved in kicking.
Famous Number 9 Players and Their Impact on the Game
Throughout the history of rugby, several number 9 players have left an indelible mark on the game, revolutionizing the position and contributing to its evolution. These players possessed exceptional skills, tactical acumen, and a deep understanding of the game, which enabled them to excel at the highest levels.
Their achievements, playing styles, and contributions have not only shaped the modern game but have also inspired generations of aspiring scrum-halves.
Notable Number 9 Players
Some of the most notable number 9 players include:
- Gareth Edwards (Wales):Widely regarded as one of the greatest scrum-halves of all time, Edwards was known for his exceptional passing, running, and vision. He played a pivotal role in Wales’s victory in the 1971 Five Nations Championship, which is often considered one of the greatest rugby matches ever played.
- Joost van der Westhuizen (South Africa):Van der Westhuizen was a dynamic and influential scrum-half who captained South Africa to victory in the 1995 Rugby World Cup. He was renowned for his speed, agility, and ability to control the tempo of the game.
- George Gregan (Australia):Gregan was a world-class scrum-half who captained Australia to victory in the 1999 Rugby World Cup. He was known for his exceptional leadership, tactical nous, and ability to orchestrate the team’s attacking play.
- Matt Dawson (England):Dawson was a key member of England’s victorious 2003 Rugby World Cup team. He was known for his quick thinking, accurate passing, and ability to snipe around the fringes of the ruck.
- Aaron Smith (New Zealand):Smith is one of the most highly-rated scrum-halves in the modern game. He is renowned for his exceptional speed, handling skills, and ability to create scoring opportunities for his teammates.
Training and Development for the Number 9 Position
Training for the number 9 position in rugby requires a comprehensive approach that focuses on developing all aspects of the player’s game. This includes physical conditioning, technical skills, and tactical awareness.
Physical Conditioning
Number 9s are required to be physically fit and strong. They must be able to withstand the rigors of the game, which includes tackling, rucking, and mauling. As such, their training should include exercises that develop strength, power, and endurance.
Technical Skills
Number 9s need to be proficient in a variety of technical skills, including passing, rucking, and decision-making. Passing is a key skill for number 9s, as they are responsible for distributing the ball to the backs. They must be able to pass accurately and quickly, both short and long distances.
Rucking is another important skill for number 9s. They must be able to clear out rucks effectively and quickly, in order to create opportunities for their team. Decision-making is also a key skill for number 9s. They must be able to make quick decisions about when to pass, ruck, or kick the ball.
Tactical Awareness
Number 9s need to have a good understanding of the game of rugby. They must be able to read the game and make decisions about when to attack and when to defend. They must also be able to work effectively with their teammates, both in attack and defense.
Tips for Improving Passing, Rucking, and Decision-Making Skills, Rugby 9 position
Here are a few tips for improving passing, rucking, and decision-making skills for number 9s:
- Passing:Practice passing with a partner, focusing on accuracy and speed. Use different types of passes, such as the flat pass, the pop pass, and the spiral pass.
- Rucking:Practice rucking with a group of players. Focus on clearing out the ruck quickly and effectively.
- Decision-making:Watch videos of rugby matches and pay attention to the decisions that the number 9s make. Try to identify the factors that influence their decisions.
Strategies and Tactics for Effective Number 9 Play

Successful number 9 players employ various strategies and tactics to control the tempo of the game, distribute the ball effectively, and create scoring opportunities. These tactics include:
Tempo Control
Number 9s can control the pace of the game by varying the speed and timing of their passes. A quick pass can accelerate the tempo, while a slower pass can slow it down. By controlling the tempo, number 9s can dictate the rhythm of the game and create opportunities for their team.
Ball Distribution
Number 9s are responsible for distributing the ball to the backs and forwards. They must make quick decisions about where to pass the ball based on the position of the opposition and the strengths of their own team. Effective ball distribution allows teams to maintain possession and create scoring chances.
Creating Scoring Opportunities
Number 9s can also create scoring opportunities for their team by running with the ball or passing it to players in space. They often act as a decoy, drawing defenders away from the ball carrier and creating gaps for other players to exploit.
The Number 9 Position in Modern Rugby
The number 9 position in rugby has evolved significantly in recent years, becoming increasingly demanding and multifaceted. This transformation can be attributed to a combination of technological advancements and rule changes that have reshaped the game’s dynamics.
Technological Advancements
The advent of video analysis and GPS tracking has revolutionized the way coaches and players approach the game. Number 9s are now expected to have a deep understanding of their own performance and that of their opponents, using data to identify areas for improvement and exploit weaknesses.
Additionally, the use of drones and other aerial footage provides a comprehensive view of the field, allowing number 9s to make informed decisions about where to distribute the ball.
Rule Changes
Rule changes such as the reduction in the number of rucks and the introduction of the scrum half box have placed greater emphasis on the number 9’s decision-making and technical skills. With fewer rucks to slow down the game, number 9s must be able to quickly assess the situation and make accurate passes to keep the ball moving.
The scrum half box has also limited the space available to number 9s, requiring them to have exceptional footwork and agility to navigate the congested area.
Evolving Responsibilities
As a result of these advancements, the responsibilities of the number 9 position have expanded beyond their traditional role as a scrum half. Modern number 9s are expected to be proficient in all aspects of the game, including:
- Scrum half play: Setting up and controlling the scrum, passing the ball to the backs, and clearing the ball from the breakdown.
- Kicking: Punting, drop kicking, and place kicking to gain territory or score points.
- Defense: Tackling, covering the backfield, and reading the opposition’s attacking patterns.
- Leadership: Communicating with the team, making decisions under pressure, and inspiring their teammates.
The number 9 position in modern rugby is a demanding and challenging one, requiring a combination of technical skills, tactical awareness, and leadership qualities. As the game continues to evolve, it is likely that the role of the number 9 will continue to adapt and expand, making it one of the most pivotal positions on the field.
Future Trends and Innovations for the Number 9 Position
The number 9 position in rugby is constantly evolving, and the future holds many exciting possibilities for this key role. In this section, we will speculate on potential future developments and innovations that may impact the number 9 position, considering the role of technology, training methods, and rule changes in shaping the future of the position.
Technology
Technology is already playing a major role in rugby, and this trend is only expected to continue in the future. Number 9s could benefit from wearable technology that provides real-time data on their performance, such as their speed, acceleration, and heart rate.
This data could be used to help them improve their training and performance, and it could also be used by coaches to make better decisions about how to use their number 9s.
Training Methods
The way that number 9s are trained is also likely to change in the future. With the increasing availability of technology, coaches will be able to use more sophisticated methods to track and analyze their players’ performance. This information can then be used to develop individualized training programs that are tailored to each player’s needs.
In addition, there is a growing emphasis on speed and agility training for number 9s, as these qualities are becoming increasingly important in the modern game.
Rule Changes
Rule changes could also have a significant impact on the number 9 position in the future. For example, if the offside line is moved back, this would give number 9s more time to make decisions and distribute the ball. Additionally, if the scrum is changed to make it more dynamic, this could create more opportunities for number 9s to run with the ball.
End of Discussion: Rugby 9 Position
The rugby 9 position continues to evolve, shaped by technological advancements and rule changes. As the game progresses, we can expect further innovations that will redefine the role and its impact on the sport. Whether you’re a seasoned player or an aspiring scrum-half, this guide provides a wealth of knowledge and inspiration to enhance your understanding and appreciation of the number 9 position.
Expert Answers
What are the primary responsibilities of the number 9 position in rugby?
The number 9 is responsible for distributing the ball from scrums, lineouts, and rucks, controlling the tempo of the game, and creating scoring opportunities.
What are the key skills required for the number 9 position?
Excellent passing skills, quick decision-making, agility, rucking ability, and leadership qualities are essential for success in the number 9 role.